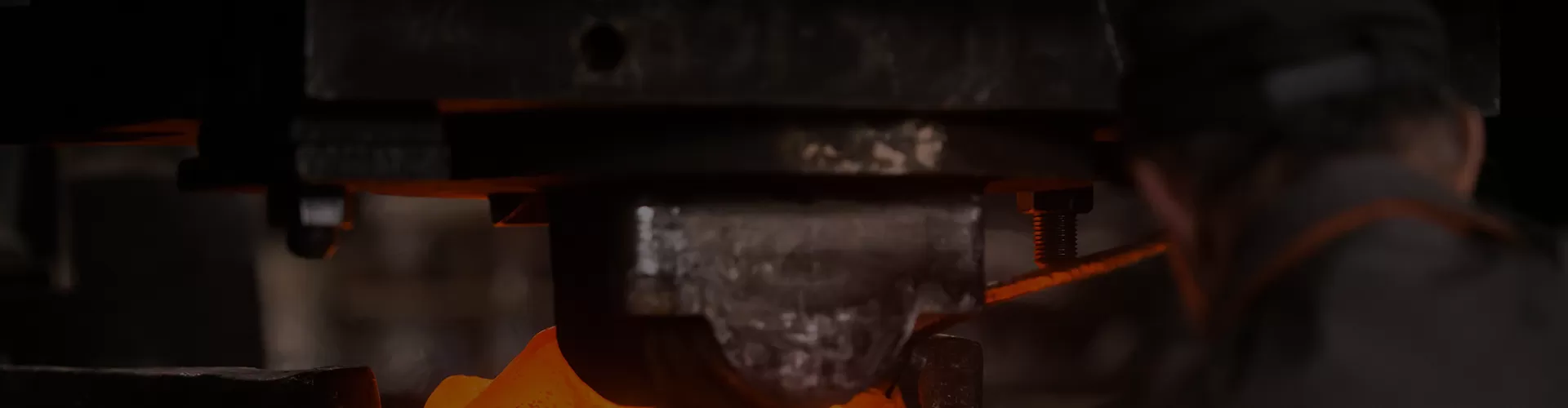
Forgings are parts that are plastically deformed by applying pressure to metal materials to obtain the desired shape and performance. In the manufacturing process, forgings can be made into blanks by forging, casting or welding, and then cut/grinded to make the required parts. In addition, in order to facilitate cutting/grinding and improve certain properties of parts, different heat treatment processes are often required in the middle. If the mechanical properties or other physical and chemical properties of the parts need to be further improved, surface treatment methods will also be used to change the surface chemical composition and distribution of the parts.
Forgings have a wide range of applications and are not limited to metal parts in mechanical equipment. For example, in addition to being widely used in the automotive industry, aluminum alloy forgings also play an important role in aerospace, drones, bicycles and other fields. In the field of aerospace, aluminum alloy forgings are used to manufacture key components such as aircraft landing gear, wings, and tails, which need to withstand huge loads and maintain stable performance in extreme environments. In the field of drones, aluminum alloy forgings have become key materials in drone manufacturing due to their light weight, high strength and corrosion resistance. In addition, in the bicycle field, aluminum alloy forgings are also widely used in the manufacture of key components such as bicycle frames, cranks, and hubs.
These application cases demonstrate the important role of forgings in improving the performance of mechanical equipment, reducing weight, and enhancing durability. They also reflect the application and development trends of forging technology in different fields.